Using a curve to animate something along a curved shape is most likely the easiest option.
- Create a (bezier) curve. ⇧ ShiftA. Shape it.
Useful operations include, Grab G, Rotate R, Scale S, Subdivide W > S, Delete X and changing the vector mode V.

Note, that the bezier curve's object center is at the origin for convenience.
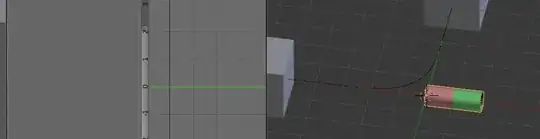
- Create a segment of the pipe object. I created if from a cylinder ⇧ ShiftA. It is exactly 2 units wide. Since the object is going to follow the path later, I added some subdivision along its width with the loopcut tool ⎈ CtrlR.
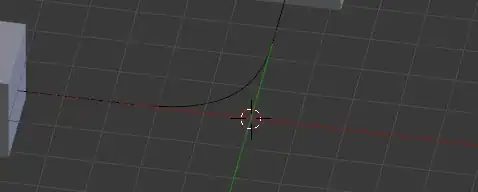
- Create two keyframes I. The first at frame 0 in my case and the second at frame 10. The translation between the two keyframes should be exactly the width of the object.
Select the keyframes assign the vector interpolation V > Vector. Then make the motion repeat, by pressing ⇧ ShiftE > Make Cyclic in the graph editor.
- Make sure the curves resolution is sufficient. Add an array modifier to the object followed by a curve modifier with the curve selected.
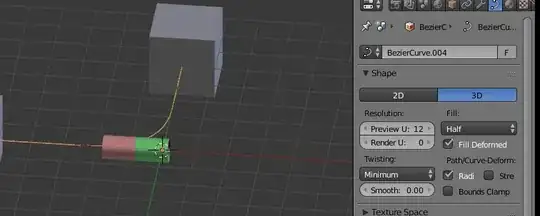
As you can see, the motion along the curved gets repeated the amount of a segment, creating the illusion of a continuously moving shape.

If the extra amount of pipe is problematic, it could be remove with a boolean modifier. Howevery, the curve could also just shape in a direction which hides the pipe from the camera's view.





