Let's suppose the mechanism is:
$$\ce{A + B <=> (AB) -> B + B}$$
Here, A is decomposed catalytically by B into B through the formation of a transient (AB) complex.
We can decompose two-step process into two reactions:
$$\ce{A + B <=>[k_1][k_2] (AB)} $$
$$\ce{(AB) ->[k_3] B + B}$$
Supposing these are "elementary" reactions, then,
$$\frac{d}{dt}(AB) = k_1[A][B] - k_2 (AB) - k_3[B]$$
If we apply the pseudo-steady state hypothesis to (AB):
$$\frac{d}{dt}(AB) = k_1[A][B] - k_2 (AB) - k_3[B] = 0$$
$$(AB) = \frac{k_1[A][B] - k_3[B]}{k_2}$$
We can additionally eliminate [A] from this equation because by stoichiometry, $[A] + (AB) + [B] = C$, where C is a constant. For simplicity, let's also suppose that (AB) will always be very low compared to [A] and/or [B]. But if (AB) is always low, we can approximate this by $[A] + [B] = C$. If so, then $[A] = C - [B]$. Substituting this into the equation above:
$$(AB) = \frac{k_1\left(C - [B] \right)[B] - k_3[B]}{k_2}$$
$$(AB) = [B]\frac{k_1\left(C - [B] \right) - k_3}{k_2}$$
Now, the rate of formation of [B] is what we are interested in. The 2nd reaction gives us the rate:
$$\frac{d}{dt}[B] = 2 k_3 (AB)$$
We can sub in the equation for (AB) we got above:
$$\frac{d}{dt}[B] = 2 k_3 [B]\frac{k_1\left(C - [B] \right) - k_3}{k_2}$$
$$\frac{d}{dt}[B] = 2 \frac{k_3}{k_2} \left([B]k_1\left(C - [B] \right) - k_3[B]\right)$$
$$\frac{d}{dt}[B] = r_B = 2 \frac{k_3}{k_2} \left( \left(k_1 C -k_3\right)[B] - k_1 [B]^2 \right)$$
$$\frac{d}{dt}[B] = r_B = 2 \frac{k_3 k_1}{k_2} \left(- [B]^2 + \left(C - \frac{k_3}{k_1}\right)[B] \right)$$
That factor in parenthesis is a quadratic in [B]. We can find when the rate will be a maximum by differentiating this term with respect to [B] and setting the result to zero.
$$-2 [B]_{maxrate} + (C - \frac{k_3}{k_1}) = 0$$
$$[B]_{maxrate} = \frac{1}{2}(C - \frac{k_3}{k_1})$$
This shows that the rate of formation of [B] will have a maximum. (Well technically an extremum but if you take the 2nd derivative you will find the extremum we found is in fact a maximum.)
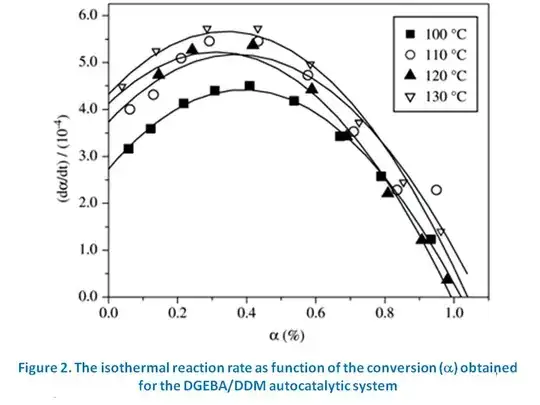
You indicated in your question that the curves you drew represented plots not of concentration, but of the reaction rate. The only curve that has a maximum rate is curve B, therefore it must be the right answer.
 An autocatalytic reaction is a reaction in which one of the products catalyses the reaction.
In general what will be the shape of curve if the rate of reaction was plotted against time for an autocatalytic reaction?
An autocatalytic reaction is a reaction in which one of the products catalyses the reaction.
In general what will be the shape of curve if the rate of reaction was plotted against time for an autocatalytic reaction?