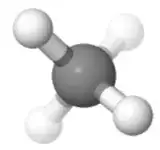
Orientation 1
Consider the orientation of methane below. The partial positive charges are distributed equally around the central atom. Comparing the left with the right side of the molecule, the top left and top right cancel each other out, and the other two are in the middle with the carbon. Comparing the top with the bottom side of the molecule, the two top hydrogen positions cancel out with the two bottom hydrogen positions. Comparing the front with the back side of the molecule, the bottom front and the bottom back hydrogen positions cancel each other out and the other two are in the plane of the paper.
For a polar molecule, the positive partial charges have to be separated from the negative ones along a direction (along the overall dipole moment, which is a vector). Here, the positive partial charges are on the outside and the negative partial charges are on the inside.

If you like vectors, you could also say the two top bond dipole moments added up point straight upwards, while the two bottom dipole moments added up point straight downwards. If you add those two up, you get a net dipole of zero.
If you like symmetry arguments, there are six mirror planes along the H-C-H planes (the left-right and the front-back are easy to see), so there can't be a dipole. The argument is as follows: If there were a dipole moment, for example left to right, and I apply the left-right mirror plane, it would have to switch directions, but the molecule is still the same. Because of this contradiction, the dipole moment has to be zero in that direction. The same argument goes for the three-fold and two-fold axis in the molecule.
Orientation 2
Due to this the component of the bond moment of the 3 downward H atoms along the line of the upper H atom would cause a net upwards bond moment which is not equal to 0.
The upper H atom is straight up, while the downward H atoms go at an angle, with the component down being 1/3 a bond length. So in that orientation, it also cancels out, but is more difficult to believe.
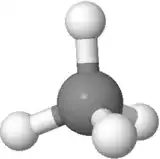
Orientation 3
In this orientation (used for Fisher projections in sugar chemistry), you can see the symmetry nicely as well one up, one down; one left, one right; two front, two back.

Orientation 4
Maybe my favorite: two up, two down, two left, two right, two front, two back - that is symmetric.