After researching this a bit more, I believe this is actually a biology question, not a physics one.
The specific term I believe you're searching for is Trichromacy, which Wikipedia defines as:
Trichromacy or trichromaticism is the condition of possessing three independent channels for conveying color information, derived from the three different cone types.1 Organisms with trichromacy are called trichromats.
Reading the Wikipedia article, it appears that the cone cells Humans (and other trichromats) come in three different variations; the different variations are sensitive to red, green, and blue light, as depicted in this image (again from Wikipedia)1:
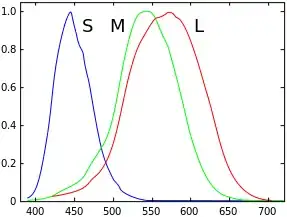
Normalized responsivity spectra of human cone cells, S, M, and L types
We've evolved these three cone types because red, green and blue are additive primaries, meaning most of the whole range of visible light can be represented by combinations of these colors. Quoting Wikipedia again:
Even the four-primary technology does not yet reach the range of colors the human eye is theoretically capable of perceiving (as defined by the sample-based estimate called the Pointer Gamut[17]), with 4-primary LED prototypes providing typically about 87% and 5-primary prototypes about 95%. Several firms, including Samsung and Mitsubishi, have demonstrated LED displays with five or six "primaries", or color LED point light sources per pixel.[18] A recent academic literature review claims a gamut of 99% can be achieved with 5-primary LED technology.
I'm not sure what the experiment you're referring to was, but I doubt it would translate nearly as nicely into sound, as RGB is based on the biology of the eye specifically.
1: Attribution: Vanessaezekowitz at en.wikipedia
