In a centre tap full wave rectifier the output voltage is half of the input(secondary coils voltage) voltage, so the power is half of power of secondary. Also in half wave rectifier the only half of the cycle is rectified but the voltage amplitude is full so the power is half of power of secondary coil. Thus I conclude that the efficiency of both half wave and full wave rectifiers are same since both of them deliver almost same power per cycle. Is my reasoning and conclusion correct?
-
You can very quickly resolve this for yourself by integrating P = IV for both input and output over a single period, and observing the difference. – uint128_t Apr 05 '16 at 03:21
-
@uint128_t What would be the qualitative way? I want yo answer it qualitatively not quantitatively. Thanks for your response – JM97 Apr 05 '16 at 03:31
-
Duplicate of Full-wave rectifier vs full-wave bridge rectifier. The full-wave bridge rectifier has two diodes in circuit all the time. The double half-wave rectifier has only one so diode losses are halved. – Transistor Apr 05 '16 at 08:01
-
@Transistor Iam not asking about difference between half wave and full wave bridge rectifier , I am asking about simple half wave rectifier(which uses only one diode) and full wave rectifier. – JM97 Sep 06 '16 at 10:29
-
Schematics are better than words. – Transistor Sep 06 '16 at 10:44
-
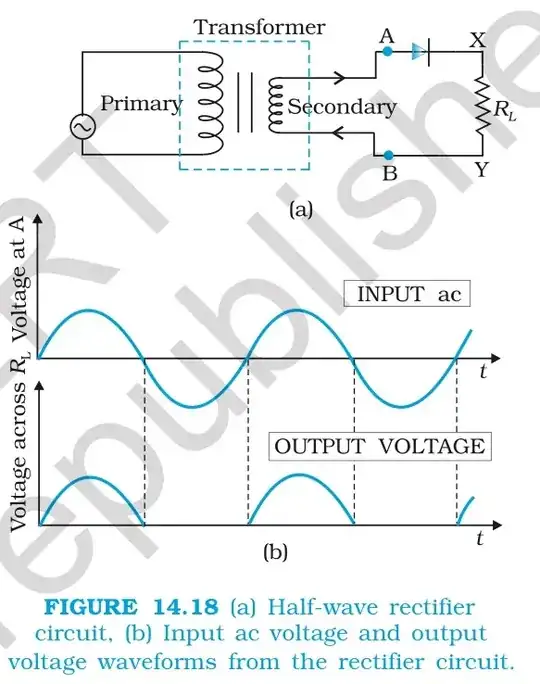
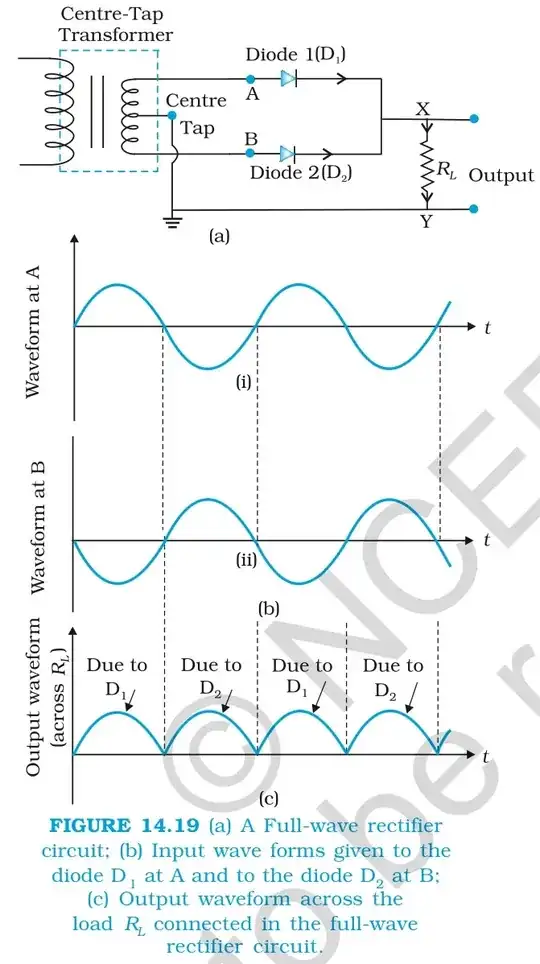
@Transistor I have posted the pictures, in second pic shouldn't be the amplitude of rectified voltage be half? – JM97 Sep 06 '16 at 10:52
-
They haven't told you the secondary voltages. The first might be 0-12 and the second 12-0-12. This would be quite common for a centre-tapped transformer. – Transistor Sep 06 '16 at 14:52
1 Answers
Start with a half wave set up with a transformer of certain primary and secondary windings. Both the primary and secondary sit idle for every other half of the cycle.
Take the same transformer, double up the secondary winding and use full wave rectifier. The two secondary windings still sit idle for every other half of the cylce while working alternately. The primary winding now works both halves of the cycle. When comparing to the first transformer, this transformer has twice the copper for the secondary, it may use the same amount of copper for the primary, the peak flux remains the same, the transformer size probably need to increase due to added copper for the secondary and the heat dissipation increase, and you can get approximately twice the power output for twice the power input.
It seems like the answer to your question depends on your definition of efficiency and what are being held constant.
- 3,544
- 1
- 11
- 6
-
I think you have misunderstood the question. It's about full-wave secondary currents generated by two different means: (1) a full bridge rectifier; (2) a centre-tapped transformer secondary with a diode in each. I think a major edit is required. – Transistor Apr 05 '16 at 08:04