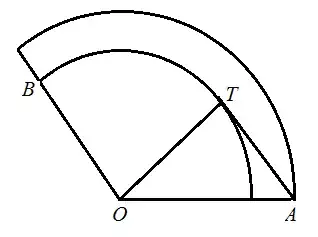
A solution can be derived by using a development (opened out cone along the slant line ABO) of the cone basis the following constraints:
- All points on the curve connecting A & B should be between the base
circle to the cone at point A & point B.
- The slope of the curve on all points should be positive, i.e.,
increasing
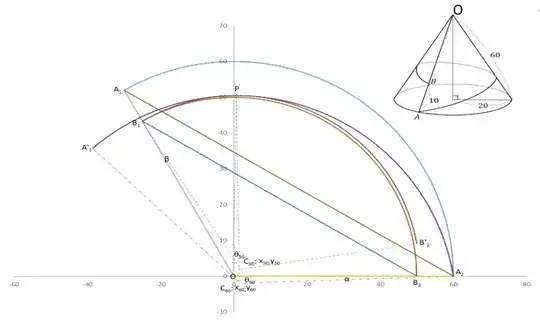
Cone development will be an arc of radius 60 and and angle 120° at arc center. Basis the above, one potential solution can be derived by rotating arc $A_1A_2$ (radius 60) counterclockwise along vertex $A_2$, rotating arc $B_1B_2$(radius 50) counterclockwise along $B_1$, finding intersection point of arc $A_1A_2$ and $B_1B_2$, such that the slope of the curve at the point of intersection is zero or horizontal. Then the total length of the path will be sum of arclength $A_2P$ and $PB_1$.
Assuming that arc $A_1A_2$ and $B_1B_2$ are rotated by angle $\alpha$ and $\beta$ respectively, then the co-ordinates for the new location of their centers $C_{60}$ and $C_{50}$ will be given by:
$$X_{60} = 60(1 - \cos(360°-\alpha))$$
$$Y_{60} = 60\sin(360° - \alpha)$$
$$X_{50} = 50(\sin(30° + \beta) - \sin30°$$
$$Y_{50} = 50(\cos30°- \cos(30°+\beta))$$
Any point on the arc $A_2A^{'}_1$ and $B_1B^{'}_2$ will be governed by the relation :
$$Y_A = Y_{60} + \sqrt{60^2 - (X_A - X_{60})^2}$$
$$Y_B = Y_{50} + \sqrt{50^2 - (X_B - X_{50})^2}$$
For the slope of the arcs at the point of intersection to be zero, the derivatives of $Y_A$ and $Y_B$ would be zero:
$$\therefore \frac{d}{dx}Y_A = 0\quad and \quad \frac{d}{dx}Y_B = 0$$
$$\therefore -\frac{X_A - 60(\cos(360°-\alpha))}{\sqrt{60^2 -(X_A - 60(1 - \cos(360°-\alpha)))^2}} = 0$$ and $$-\frac{X_B - 50(\sin(30+\beta)-\sin30°)}{\sqrt{50^2 - (X_B - 50(\sin(30°+\beta) - \sin30°))^2}} = 0$$
Solving the above two equations, gives the 'X' co-ordinate for the point of intersection as:
$$X_A = 60(1-\cos(360°-\alpha)) = X_{60}$$ and $$ X_B = 50(\sin(30°+\beta) - \sin30°) = X_{50}$$
Substituting above $X_A$ and $X_B$ values in equations for $Y_A$ and $Y_B$ above, gives:
$$Y_A = 60(1+\sin(360°-\alpha))$$ and $$Y_B = 50(\cos30° - \cos(30°+\beta) + 1)$$
Now as these are the co-ordinates for the point of intersection of the arcs:
$$\therefore X_A = X_B\quad and \quad Y_A = Y_B$$
Solving for $\alpha$ and $\beta$, gives:
$$\alpha = 9.158°\, and\; \beta = 1.017°$$
Now as the X co-ordinates for both arc centers and the point of intersection are the same, arc centers and point of intersection are on a single straight line parallel to Y-axis. Hence:
Angle of arc $A_2P$ at its center $= 90°-\alpha = 90°-9.158° =
80.842° = 1.41096$ radians
Angle of arc $PB_1$ at its center $= 30°+\beta = 30°+1.017° =
31.017° = 0.54135$ radians
Hence, the total distance from A to B around the cone:
$=$ Arclength $A_2P +$ Arclength $PB_1$
$=A_1A_2$ arc radius
$\times$ Arc angle $+\;B_1B_2$ arc radius $\times$ Arc
angle $=60\;\times\;1.41096\;+50\;\times\;0.54135=111.725$