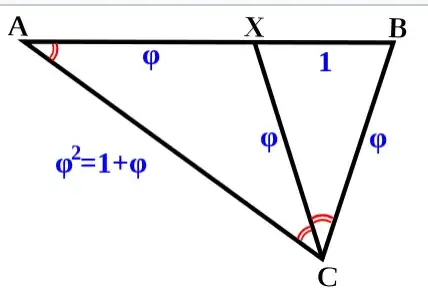
As shown on Wikipedia's article about golden ratio (letters in the blockquote indicate points on the picture provided by Wikipedia):
If angle BCX = α, then XCA = α because of the bisection, and CAB = α because of the similar triangles; ABC = 2α from the original isosceles symmetry, and BXC = 2α by similarity. The angles in a triangle add up to 180°, so 5α = 180, giving α = 36°. So the angles of the golden triangle are thus 36°-72°-72°. The angles of the remaining obtuse isosceles triangle AXC (sometimes called the golden gnomon) are 36°-36°-108°.
From the given above (in the question) $AH=TH= \phi$ and $m(\angle AHT)=36°$, So by using Law of cosines:
$${AT}^2={AH}^2+{TH}^2-2(AH)(TH)(\cos {\angle AHT}) \\ {AT}^2={\phi}^2+{\phi}^2-2(\phi)(\phi)(\cos {36°}) \\ {AT}^2=2{\phi}^2-2\phi^2 \cdot \cos {36°} \\ {AT}^2=2 \left( {\frac {3+ \sqrt 5}{2}} \right) -2 \left( {\frac {3+ \sqrt 5}{2}} \right) (\cos {36°})=1 \\ AT=\sqrt 1 =1$$
Similarly,
$${AC}^2=2 {\phi}^2-2{\phi}^2(\cos 108°)={\phi}^4 \\ AC = {\phi}^2$$
Now you know it, law of cosines is the trick in such questions.
I hope my answer helps you !
Another solution:-
You can use trigonometrical functions to get the height of any of the two triangles and then use Pythagoras theorem to find other sides (in each triangle).
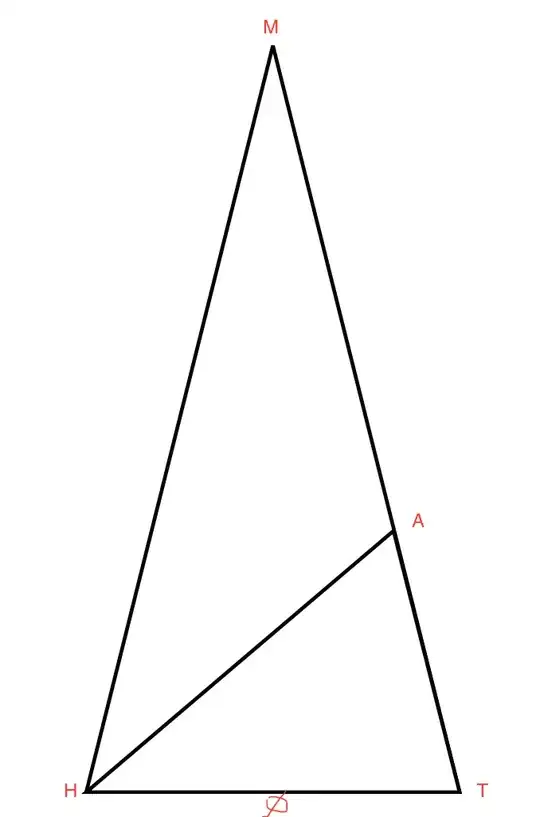 Find the lengths of both lines AT and MT.
Find the lengths of both lines AT and MT.