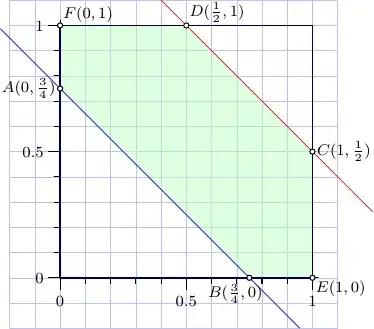
Find the area of the region $\{(x,y):0\leq x \leq 1, 0 \leq y\leq 1, 3/4\leq x+y\leq 3/2\}$ (using definite integration).
I cannot understand how to find this area. I have graphed the lines and found out the required region. I found the definite integral $\int_{0}^{1} (3/2-y)-(3/4-y)dy$ but it is yielding an extra areas. How do I find the area of the region?