Now also asked on MathOverflow and answered affirmatively there.
Let there be $n$ pairs of shoes in a box.
The the probability that from the $r \le n$ shoes I am taking out of the box there are exactly $p$ pairs is given by
\begin{equation*}
\mathbb{P}_{n}^{(r)}(p)
= \frac{\binom{n}{p} \binom{n-p}{r-2p} 2^{r-2p}}{\binom{2n}{r}}.
\end{equation*}
For $n = 15$ and $r \in \{6,8,10\}$. The function (assuming the continuous factorial equivalents) looks like this:
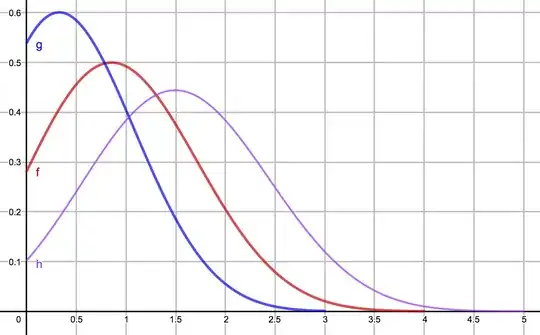
I am interested in finding the area under that curve, namely $$\int_{0}^{\frac{r}{2}} \frac{\binom{n}{p} \binom{n-p}{r-2p} 2^{r-2p}}{\binom{2n}{r}} \ \text{d}p$$ According to numerical estimates in the comments I suspect that it converges to 1 for $n = r \to \infty$.
I consulted this question but could derive how that would help me.
I also thought about writing the first product of binomial coefficients as $$ \binom{n}{n - p}\binom{n - p}{r - 2p} $$ which is similar to the form $\binom{f(x)}{f(y)} \binom{f(y)}{f(x)}$ mentioned in this question.