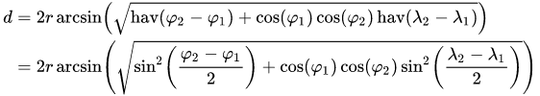As an aviator I'm familiar with the concept of great-circle navigation because when we fly a route between 2 points on the globe we know the shortest distance between these two points is the great circle distance.
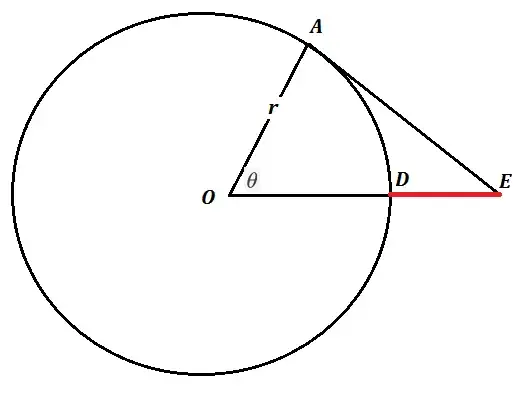
I'm developing a navigation app in Google Earth and I need to calculate the shortest distance from the surface of the "spherical" Earth to any point on the tangent line through A (origin) when flying the great circle path.
Also, I'm using a mean earth radius of 6,371.009 km for WGS84 ellipsoid.
Just to be clear, I'd like to refer to the diagram in the following link:
http://www.alaricstephen.com/main-featured/2017/5/22/the-haversine-formula
I use the Haversine formula to calculate the distance, d, between the points A and D (see diagram). What I'd like to calculate is the distance D to E as a function of d.
In the diagram this is referred to as the external secant (exsec) which is the portion DE of the secant exterior to the circle.