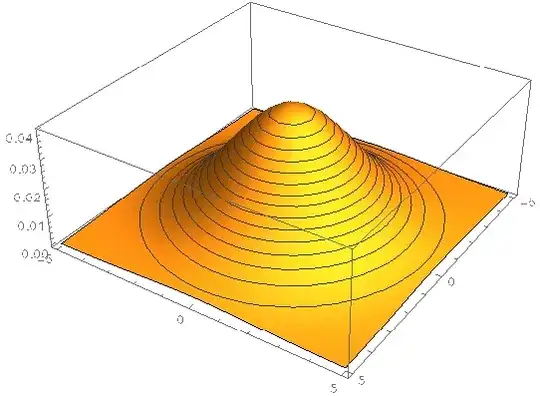
Suppose that $X, Y \sim N(0, 4)$ are independent and normally distributed random variables.
My question is how to find $P(2 \leq |X| + |Y| \leq 3)$?
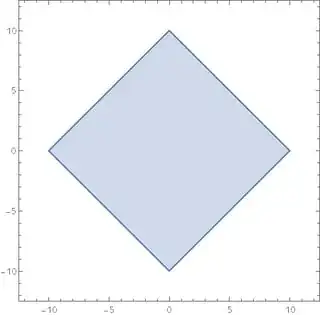
Probably, the first step is to try to solve a more general task and find the distribution of $Z := |X| + |Y|$, i.e. find $F_Z(t) = P(Z \leq t) = P(|X| + |Y| \leq t)$ for $t > 0$.
The straightforward way would be to compute the integral:
$$\int\limits_{|x| + |y| \leq t} \dfrac{1}{8\pi} e^{-(x^2 + y^2)/4}dxdy$$
This task seems to be non-trivial because the resulting integrals end up being hard to calculate. Assuming the function $\Phi(t) = \int\limits_{-\infty}^{t} \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-x^2/2}dx$ is known, the integral above requires computing something like $\int\limits_{0}^{t}e^{-x^2/4}\Phi(x) dx$ which I'm not sure how to compute with simple calculus tools that I know.
Maybe it is easier than I think or maybe there is just a different better way of solving this.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.