An alternative approach, more accurate and efficient, is as follows. Consider the two ODEs in the question, slightly restructured.
eqn1 = D[D[psi[r], {r, 2}] (1 - xx1*D[psi[r], {r, 2}]^2), {r, 2}] +
D[p[r], {r, 1}] - D[psi[r], {r, 2}] == 0
eqn2 = D[p[r], {r, 2}] + D[psi[r], {r, 2}] (1 - xx1*D[psi[r], {r, 2}]^2) == 0
psi[r], psi'[r], and p[r] do not enter explicitly into these equations. Therefore, define qsi[r] as Sqrt[xx1] psi''[r] and q[r] as p'[r], so that the equations become
qn1 = D[qsi[r] (1 - qsi[r]^2), {r, 2}] + q[r] - qsi[r] == 0
qn2 = D[q[r], {r, 1}] + qsi[r]*(1 - qsi[r]^2) == 0
A modest amount of algebra shows that the boundary conditions become
NIntegrate[q[r], {r, -1, 3/2}] + Sqrt[xx1] == 0
NIntegrate[qsi[r], {r, -1, 3/2}] == 0
NIntegrate[r qsi[r], {r, -1, 3/2}] + 4 Sqrt[xx1] == 0
Next, define t[r] as qsi[r] - qsi[r]^3 to eliminate the singularity in qn1 at qsi[r] = 1.
qsi /. FullSimplify[Solve[t == qsi - qsi^3, qsi, Reals],
-(2/(3 Sqrt[3])) < t < 2/(3 Sqrt[3])]
(* {Root[t - #1 + #1^3 &, 1], Root[t - #1 + #1^3 &, 2], Root[t - #1 + #1^3 &, 3]} *)
Plot[%, {t, -(2/(3 Sqrt[3])), 2/(3 Sqrt[3])}, AxesLabel -> {t, qsi},
PlotLegends -> "Expressions"]

With the second branch of this final transformation, the equations and boundary conditions become
qn1 = D[t[r], {r, 2}] + q[r] - Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] == 0
qn2 = D[q[r], {r, 1}] + t[r] == 0
NIntegrate[q[r], {r, -1, 3/2}] + Sqrt[xx1] == 0
NIntegrate[Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2], {r, -1, 3/2}] == 0
NIntegrate[r Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2], {r, -1, 3/2}] +4 Sqrt[xx1] == 0
The second and third integrals are real only for -(2/(3 Sqrt[3])) < t < 2/(3 Sqrt[3]). The absence of answers to 110534 suggests that this requirement cannot be imposed using NDSolve with Method -> "Shooting". Instead, use FindRoot directly.
xx1 = 8.7677 10^-3;
qn1 = D[t[r], {r, 2}] + q[r] - Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] == 0;
qn2 = D[q[r], {r, 1}] + t[r] == 0;
qns = {qn1, qn2, t[-1] == a, t'[-1] == b, q[-1] == c};
st = ParametricNDSolve[qns, {t, q}, {r, -1, 3/2}, {a, b, c}, MaxStepFraction -> 1/1000];
int1[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[q[a, b, c][r] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}] + Sqrt[xx1];
int2[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}];
int3[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[r Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}] + 4 Sqrt[xx1];
qval = Quiet@FindRoot[{int1[a, b, c], int2[a, b, c], int3[a, b, c]},
{a, 0.3848882573269839`, .3, 2/(3 Sqrt[3]) }, {b, -0.4895029166208631`},
{c, 0.0935952879725864`}, MaxIterations -> 500]
Unevaluated[{int1[a, b, c], int2[a, b, c], int3[a, b, c]}] /. %
Plot[Evaluate[{Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2],
t[a, b, c]'[r]/(1 - 3 Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2]^2),
q[a, b, c][r]} /. st /. %%], {r, -1, 3/2}]
Plot[Evaluate[{t[a, b, c][r], t[a, b, c]'[r], q[a, b, c][r]} /. st /. %%%], {r, -1, 3/2},
AxesLabel -> {r, "qsi, qsi', q"}]
(* {a -> 0.384898, b -> -0.489519, c -> 0.0935965} *)
(* {-9.71445*10^-17, -6.99907*10^-16, -8.88178*10^-16} *)

This particular xx1 has been chosen to yield t[-1] = a = 0.384898, which is very close to 2/(3 Sqrt[3]), indicating that xx1 = 8.7677 10^-3 is a very good approximation to the upper bound on xx1, above which the boundary conditions cannot be satisfied.
psi[r] and p[r] can be obtained by straightforward integration of qsi[r] and q[r].
sp = NDSolve[{D[psi[r], {r, 2}] == Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2]/Sqrt[xx1] /. st
/. qval, D[p[r], r] == q[a, b, c][r]/Sqrt[xx1] /. st /. qval,
psi[-1] == -3/4, psi'[-1] == -1, p[-1] == 1}, {psi, p}, {r, -1, 3/2}];
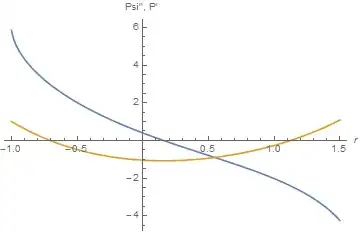
Plot[Evaluate[{psi[r], p[r]} /. sp], {r, -1, 3/2}, AxesLabel -> {r, "psi, p"}]

Addendum: Direct calculation of xx1 upper bound
Determining the upper bound on xx1 turns out to be surprisingly easy, given a good initial guess. Set t[-1] == 2/(3 Sqrt[3]), the maximum value it can assume, and vary xx1 with FindRoot
Clear[xx1];
qn1 = D[t[r], {r, 2}] + q[r] - Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] == 0;
qn2 = D[q[r], {r, 1}] + t[r] == 0;
qns = {qn1, qn2, t[-1] == 2/(3 Sqrt[3]), t'[-1] == b, q[-1] == c};
st = ParametricNDSolve[qns, {t, q}, {r, -1, 3/2}, {b, c}, MaxStepFraction -> 1/1000];
int1[xx1_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[q[b, c][r] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}] + Sqrt[xx1];
int2[xx1_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[Root[t[b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}];
int3[xx1_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[r Root[t[b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}] + 4 Sqrt[xx1];
qvql = Quiet@FindRoot[{int1[xx1, b, c], int2[xx1, b, c], int3[xx1, b, c]},
{xx1, 8.7677 10^-3}, {b, -0.4895029166208631`}, {c, 0.0935952879725864`},
MaxIterations -> 500]
Unevaluated[{int1[xx1, b, c], int2[xx1, b, c], int3[xx1, b, c]}] /. %
Plot[Evaluate[{Root[t[b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2],
t[b, c]'[r]/(1 - 3 Root[t[b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2]^2),
q[b, c][r]} /. st /. %%], {r, -1, 3/2}, AxesLabel -> {r, "qsi, qsi', q"}]
(* {xx1 -> 0.00876784, b -> -0.489523, c -> 0.0935967} *)
(* {2.26208*10^-15, 1.27339*10^-13, 1.94289*10^-14} *)
Thus, the upper bound is xx1 = 0.00876784. The corresponding Plot is indistinguishable from the second to the last one above.
Second Addendum: Solutions above the "upper bound"
As suggested by MMM, it is possible - although more difficult - to obtain solutions for xx1 greater than the purported upper bound given in the last section. Doing so requires using branch 3 and often branch 1, as well as branch 2 of the t transform plotted in the first figure. The following code accomplishes this.
Clear[st]; r1 = -1; r2 = 3/2; xx1 = 2.5 10^-2;
qns = {D[q[r], {r, 1}] + t[r] == 0, t[-1] == a, t'[-1] == b,
q[-1] == c, n[-1] == If[xx1 > 0.008767841540390384`, 3, 2],
WhenEvent[t[r] > 2/(3 Sqrt[3]) - 10^-4, {n[r] -> 2, t'[r] -> -t'[r], r1 = r, r2 = 3/2}],
WhenEvent[t[r] < -2/(3 Sqrt[3]) + 10^-4, {n[r] -> 1, t'[r] -> -t'[r], r2 = r}]};
st = ParametricNDSolve[{qns, D[t[r], {r, 2}] + q[r] == Root[t[r] - #1 + #1^3 &, n[r]]},
{t, q, n}, {r, -1, 3/2}, {a, b, c}, MaxStepFraction -> 1/1000,
DiscreteVariables -> {n[r] \[Element] {1, 2, 3}}];
int1[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
Chop@NIntegrate[q[a, b, c][r] /. st, {r, -1, 3/2}] + Sqrt[xx1];
int2[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 3] /. st, {r, -1, r1}] +
NIntegrate[Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, r1, r2}] +
NIntegrate[Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 1] /. st, {r, r2, 3/2}];
int3[a_?NumericQ, b_?NumericQ, c_?NumericQ] :=
NIntegrate[r Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, -1, r1}] +
NIntegrate[r Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2] /. st, {r, r1, r2}] +
NIntegrate[r Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 1] /. st, {r, r2, 3/2}] + 4 Sqrt[xx1];
qval = Quiet@FindRoot[{int1[a, b, c], int2[a, b, c], int3[a, b, c]},
{a, 0.26367683907672707`, -2/(3 Sqrt[3]), 2/(3 Sqrt[3])},
{b, 0.40781910948554423`}, {c, 0.0918387339602277`}]
Unevaluated[{int1[a, b, c], int2[a, b, c], int3[a, b, c]}] /. %
Plot[Evaluate[{Piecewise[{{Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2],
r1 < r < r2}, {Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 3],
r <= r1}, {Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 1], r2 <= r}}],
t[a, b, c]'[r]/(1 - 3 Piecewise[{{Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 2],
r1 < r < r2}, {Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 3],
r <= r1}, {Root[t[a, b, c][r] - #1 + #1^3 &, 1], r2 <= r}}]^2),
q[a, b, c][r]} /. st /. %%], {r, -1, 3/2}, AxesLabel -> {r, "qsi, qsi', q"}]
Plot[Evaluate[{t[a, b, c][r], t[a, b, c]'[r], q[a, b, c][r]} /.
st /. %%%], {r, -1, 3/2}, AxesLabel -> {r, "t, t', q"}, Exclusions -> {r1, r2}]
(* {a -> 0.219976, b -> 0.368499, c -> 0.0839676} *)
(* {-1.38255*10^-10, 4.27128*10^-10, 4.16582*10^-10} *)


t and t'are included for completeness in the second plot.
The guess a, equal to t[-1], needed to obtain a solution becomes smaller as xx1 becomes larger, and some experimentation is necessary to obtain a sufficiently good value. Even then, computing the curves for a given xx1 takes several minutes on my computer.








xx1as large as8.65 10^-3. However, asxx1increases,psi'''[-1]becomes quite large in absolute value, and probably become singular for sufficiently largexx1. – bbgodfrey Mar 18 '16 at 00:58p[r],psi[r], andpsi'[r]do not appear in the ODEs themselves and only in the boundary conditions, the ODEs can be rewritten in terms ofq[r]in place ofp'[r]andqsi[r]in place ofpsi''[r], in which case the boundary conditions are replaced by integrals over the solutions forq[r]andqsi[r]. This approach could very well be more accurate. – bbgodfrey Mar 18 '16 at 04:21xx1about the solution forxx1 = 0and then solve the linearized equations. Of course, this approach would break down well beforexx1 = 1. – bbgodfrey Mar 18 '16 at 04:24XX1=c*0.045wherecis the continuation. – zhk Mar 18 '16 at 17:38c, so that the actual value ofXX!can be determined? – bbgodfrey Mar 18 '16 at 23:54cis a continuation parameter, which is used in thedsolvecommand ascontinuation=c. – zhk Mar 19 '16 at 13:43XX1=c*0.0045in your earlier comment? Thanks. – bbgodfrey Mar 19 '16 at 16:41