Clear[f]
f[x_] = (1 - 3*(x + 1)^3)/(x^4 + 1)*(x - 2);
roots = x /. Solve[f[x] == 0, x]
(* {2, -1 + 1/3^(1/3), -1 - (1 - I Sqrt[3])/(2 3^(1/3)), -1 - (1 + I Sqrt[3])/(
2 3^(1/3))} *)
The radicals can be expressed as Root objects
roots // RootReduce
(* {2, Root[2 + 9 #1 + 9 #1^2 + 3 #1^3 &, 1],
Root[2 + 9 #1 + 9 #1^2 + 3 #1^3 &, 3], Root[2 + 9 #1 + 9 #1^2 + 3 #1^3 &, 2]} *)
And low-order Root objects can be expressed by radicals using ToRadicals
% // ToRadicals
(* {2, -1 + 1/3^(1/3), -1 - (1 - I Sqrt[3])/(2 3^(1/3)), -1 - (1 + I Sqrt[3])/(
2 3^(1/3))} *)
% === roots
(* True *)
Either radicals or Root objects can be converted to approximate numeric values by N
roots // N
(* {2., -0.306639, -1.34668 + 0.600468 I, -1.34668 - 0.600468 I} *)
critPts = x /. Solve[f'[x] == 0, x]
(* {Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 1],
Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 2],
Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 3],
Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 4],
Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 5],
Root[16 + 18 #1 - 9 #1^2 - 28 #1^3 - 48 #1^4 - 18 #1^5 + 3 #1^6 &, 6]} *)
The order of these polynomials are too high to express as radicals but can be expressed as approximate numeric values with N
critPts // N
(* {-1.57785, -0.714464, 0.703213, 8.11693, -0.263913 - 0.871319 I, -0.263913 +
0.871319 I} *)
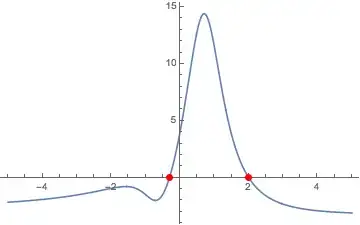
Plot[f[x], {x, -3, 10}, PlotRange -> All,
Epilog -> {AbsolutePointSize[6], Red,
Point[{#, f[#]} & /@
Cases[critPts, _?(Im[#] == 0 &)]],
Blue, Point[{#, f[#]} & /@
Cases[roots, _?(Im[#] == 0 &)]]},
PlotLegends -> PointLegend[{Red, Blue},
{"Critical Point", "Root"}]]





- As you receive help, try to give it too, by answering questions in your area of expertise.
- Take the tour and check the faqs!
- When you see good questions and answers, vote them up by clicking the gray triangles, because the credibility of the system is based on the reputation gained by users sharing their knowledge. Remember to accept the answer, if any, that solves your problem, by clicking the checkmark sign!
– Oct 12 '16 at 16:58Rootsrepresents these roots for potential further processing. If you want numerical approximations, you can either 1) wrap theRootscommand inN, or 2) useNSolveto get "actual numbers". – corey979 Oct 12 '16 at 17:12