The data looks smooth enough. The glitch is due to the parabola with a vertical axis that fits the last three points. What if the data was rotated? The glitch should go away. But, rotated by what angle and around which point?
Suppose we have the abscissa $x_0$ and we want the interpolant $y_0$. Then the point we will rotate the data about will be $(x_0,0)$ and the angle will be 45 degrees, CCW. This choice makes the math simple enough to demonstrate feasibility of this approach.
Here's the code for a rotating interpolation function and the code for two test plots.
rifn[x0_, pts_] :=
Block[{\[Theta] = \[Pi]/4, fwd, rot, ifn, pt0, x1, x, y1},
fwd = {{Cos[\[Theta]], -Sin[\[Theta]]}, {Sin[\[Theta]],
Cos[\[Theta]]}};
rot = Dot[fwd, # - {x0, 0}] & /@ data;
ifn = Interpolation[rot, InterpolationOrder -> 2];
x1 = x /. First[FindRoot[ifn[-x] == x, {x, 0}] // Quiet];
y1 = ifn[-x1];
pt0 = fwd.{x1, y1} + {x0, 0};
Last[pt0]
]
Plot[rifn[x, data], {x, 0, 0.171663},
Epilog -> {Red, Point@data}, AspectRatio -> GoldenRatio]
Plot[{rifn[x, data],
Interpolation[data, InterpolationOrder -> 2][x]},
{x, 0.15, 0.171663},
Epilog -> {Red, Point@data}, AspectRatio -> GoldenRatio]
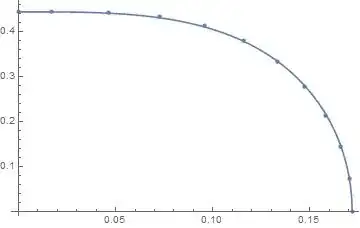
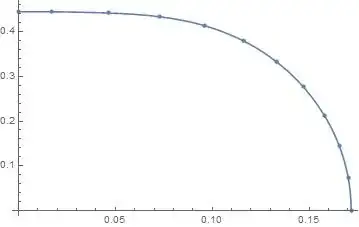
The first plot shows the smoothness of interpolation over the entire range of the data. The second plot zooms in on an interval that contains the glitch. The rotating interpolation function appears to be feasible.

How does it work? First, we define the rotation matrix fwd that rotates the data CCW. The second line takes each point in the data, shifts is by the amount {x0,0} and the applies the rotation matrix. The third line uses the built-in Interpolation function. The fourth line requires a little sketch to explain.
The sketch attempts to show 4 data points, the abscissa $x_0$ and the desired interpolant $y_0$. When the data points are rotated the new abscissa will be $x_1$ and the new interpolant will be $y_1$. Since we are rotating 45 degrees, we will have $x_1=y_1$. We use FindRoot to find the abscissa that satisfies this condition. Thus, the angle is hardwired into the argument of FindRoot.
Having found $x_1$, we can find $y_1$ either by interpolation or by geometry. Finally, we rotate the point $(x_0,y_0)$ back (using the same fwd rotation matrix) and shift it back. Thus, inside the rifn[] function, pt0 is the interpolated point $(x_0,y_0)$ that we were looking for. The rifn function returns only $y_0$.
This approach appears to be quite feasible for the given data.
 There is a noticeable bump in the plot around x = 0.165. It looks like the interpolating function is not differentiable around that point (that is strange, as the differentiability is on of the basic assumptions when dealing with interpolations of order 2 and higher). What causes this behaviour? Dataset itself looks completely "normal" everywhere
There is a noticeable bump in the plot around x = 0.165. It looks like the interpolating function is not differentiable around that point (that is strange, as the differentiability is on of the basic assumptions when dealing with interpolations of order 2 and higher). What causes this behaviour? Dataset itself looks completely "normal" everywhere



Method -> "Spline". – Apr 09 '17 at 20:42for argument in some range between two points (x1, x2), the function is ax^2+bx+c. Determine the coefficients from three equations: value of interpolation must match function values in points x1, x2 and derivative of interpolation must be continuous. So to have interpolation of order two, one has to provide at least three points. Derivative at the ending points can be set by hand. For me it's obvious f'(0) = 0, f'(end of the interval) = infinity (like for function sqrt(1-x)).
– user16320 Apr 09 '17 at 21:00f = Interpolation[Table[{1 - i^2, i}, {i, 0, 1, 0.1}], InterpolationOrder -> 2]; Plot[f[x], {x, 0, 1}] ListPlot[f]
you will see that even though the data (square root) is as precise as possible (ie we know what the function is), the interpolation has a bump. You certainly can't say that this is some kind of error in the data, can you?
– user16320 Apr 09 '17 at 21:15ifn = Evaluate@Sqrt@Interpolation[Transpose@{data[[All, 1]], data[[All, 2]]^2}][#] &– Michael E2 Apr 09 '17 at 21:39InterpolationOrder -> 2) interpolant? – J. M.'s missing motivation Apr 09 '17 at 23:17InterpolationOrder -> 2vs. fitting....Or do you mean theFunctionnotation# &? – Michael E2 Apr 09 '17 at 23:49Plot[ifn[x],{x,0,0.171663}]instead. – Apr 10 '17 at 00:24Function(orifn = expr &) has the attributeHoldAll, which means normallyexprwon't be evaluated until the function is called, e.g.ifn[x]is evaluated.Evaluateoverrides that, and inEvaluate[expr] &(or what is the same thing,Evaluate@expr &),expris evaluated first and passed toFunction. In my case, it means that the interpolating function will be constructed only once, at the timeifnis defined, instead of every timeifn[x]is called. It's discussed briefly here. HTH – Michael E2 Apr 10 '17 at 10:03