Suppose I want to solve an ODE with a DiracDelta source term. In the following example, DSolve does it correctly while NDSolve (understandably) misses the Delta and provides the solution corresponding to a zero right hand side:
ex = y /. First[DSolve[{y'[x] + y[x] == DiracDelta[x - 1], y[2] == 1}, y, x]];
nu = y /. First[NDSolve[{y'[x] + y[x] == DiracDelta[x - 1] , y[2] == 1}, y, {x, 0.1, 2}]];
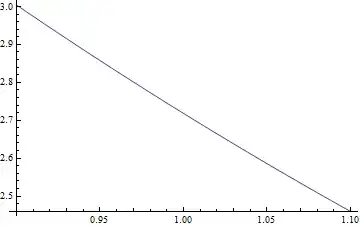
Plot[ex[t], {t, 0.9, 1.1}]
Plot[nu[t], {t, 0.9, 1.1}]
Plot of DSolve solution
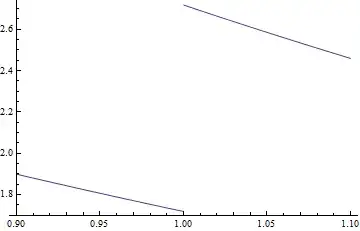
Plot of NDSolve Solution
Is there anyway around this using NDSolve (without converting the system to integral form)? I'd be happy to lend NDSolve a hand, say by telling it to look for a piecewise continuous solution ({x,0.1,1,2}) and provide jump conditions (in the above example y(1+eps) - y(1-eps) == 1).
(DSolve does not solve the real equations I am really interested in... they are multidimensional, nonlinear, and a bit too messy to replicate here).

Mathematica 9, there are capabilites to handle such problems in a seamless way. Take a look at this http://www.wolfram.com/mathematica/new-in-9/advanced-hybrid-and-differential-algebraic-equations/ – Artes Dec 01 '12 at 23:05