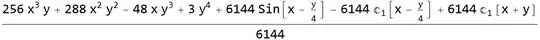You can't solve this analytically. So you need to try numerical solution. But to see the issue, you can start by solving it analytically without the condition
$$
\frac{\partial}{\partial x}f(x,y)|_{y=x} = 0
$$
Then after solving it, make an equation to solve the constant of integration $c_1$. In this case, since this is a PDE and not ODE, the constant of integration is an arbitrary function $c_1$. This makes it not possible to solve for it:
ClearAll[f, x, y];
pde = D[f[x, y], {x, 2}] + 3*D[D[f[x, y], x], y] - 4*D[f[x, y], {y, 2}] == x*y
bc = f[x, 0] == Sin[x]
sol = DSolveValue[{pde, bc}, f[x, y], {x, y}]
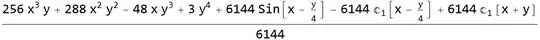
Now apply the second "condition"
der = D[sol, x] /. y -> x
eq = der == 0

Now if you can solve for this arbitrary function $c_1$ from the above equation, then you have solved the PDE.
But it is not possible to solve for $c_1$ above. But may be someone can find a trick to do it. Notice that $c_1$ is actually a function of $x,y$ by looking at the solution above.