Is there a command to find the poles of a function $f=f(z)$?
example: let $$f(z) = \frac{1}{z^2-1}$$ then we know that the poles are at $z=\pm 1$ but is there a special command in mathematica to do this?
Is there a command to find the poles of a function $f=f(z)$?
example: let $$f(z) = \frac{1}{z^2-1}$$ then we know that the poles are at $z=\pm 1$ but is there a special command in mathematica to do this?
There is a special function for this: it's called TransferFunctionPoles. For the case you asked for:
TransferFunctionPoles[TransferFunctionModel[{{1/(z^2 - 1)}}, z]]
which returns the expected answer that there are two poles at
{{{-1, 1}}}
TransferFunctionPoles can also handle multivariable input/output models of the kind that control engineers like to play with, including symbolic transfer functions and time-delay systems. There are a number of related commands including TransferFunctionZeros, TransferFunctionModel, StateSpaceModel ways of converting continuous to discrete models, and special plotting functions like RootLocusPlot and NyquistPlot.
Tan[z]. It complains about polynomial numerators and denominators. Is this method restricted to rational functions?
– Michael E2
Jun 12 '13 at 17:18
Since V 13.0 we have FunctionPoles:"
From the documentation: "FunctionPoles returns a list of pairs {pole, multiplicity}."
f = 1 / (z^2 - 1);
FunctionPoles[f, z]
{{-1, 1}, {1, 1}}
To only get the poles:
{a, b} = FunctionPoles[f, z][[All, 1]]
{-1, 1}
Plot[f, {z, -10, 10},
Epilog -> {Red, Dashed, InfiniteLine[{a, 0}, {0, 1}], InfiniteLine[{b, 0}, {0, 1}]},
PlotRange -> Automatic]
Use FunctionDomain to find the real domain, then remove the whole line from the domain found. What is left are the poles. (this is all on the real line)
ClearAll[f,z]
f = 1/(z^2-1)
domain = FunctionDomain[f,z,Reals];
wholeLine = -Infinity < z < Infinity;
Reduce[ wholeLine && Not[domain],z,Reals]

f = Tan[z];
domain = FunctionDomain[f,z,Reals];
wholeLine = -Infinity<z<Infinity;
Reduce[ wholeLine && Not[domain],z,Reals]
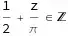
It works for 2D also
ClearAll[f,x,y]
f = 1/x Log[y];
domain = FunctionDomain[f,{x,y},Reals];
wholeLine = {-Infinity<x<Infinity && -Infinity<y<Infinity};
Reduce[Join[wholeLine,{Not[domain]}],{x,y},Reals]

Solve[1/f[z] == 0, z]? – Michael E2 Jun 12 '13 at 15:38Tan[]:Reduce[1/Tan[x] == 0, x]]. Should work nicely for rational functions, too. – J. M.'s missing motivation Jun 12 '13 at 15:43Solve[], as @Michael recommended.Reduce[]takes a bit more effort internally... – J. M.'s missing motivation Jun 12 '13 at 15:55Solve[Denominator[f[z]]==0,z], but I would say this question is good because I also expect something much easier and more automatic (in case one doesn't want to organize the expression off[z]). – Leo Fang Jun 12 '13 at 16:31