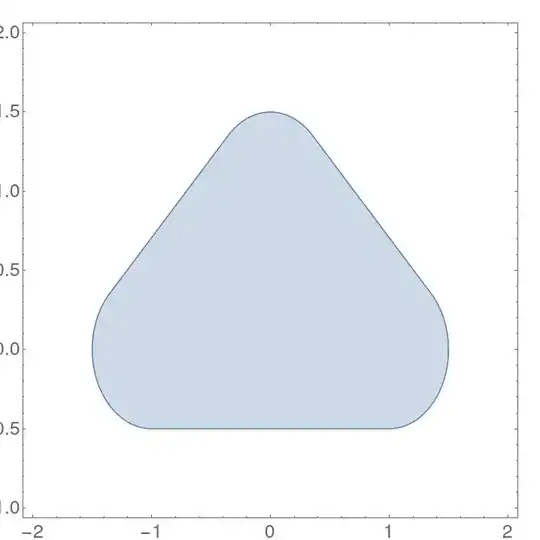
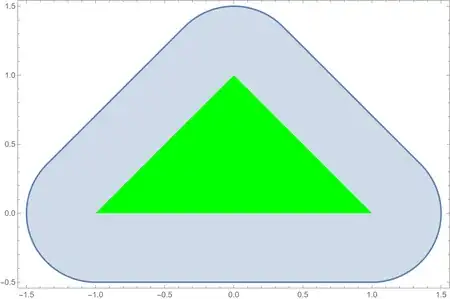
I would like to integrate the function f(x,y) = x^2 + y^2 over the epsilon-neighborhood of the triangle {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}}. By epsilon-neighborhood, I mean the set of points which are closer to the triangle than epsilon (let's say epsilon = 0.5).
I do not know what is the best way to define such a region, how to plot it and how to integrate a function over it. I have tried the following code, but it gives back the incorrect result 0.3 even for the area (I don't know why). It seems that the same code works correctly for a Rectangle[{-1, -1}, {1, 1}], somehow.
RegT = Region[Triangle[{{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}}]]
(* Define the epsilon-neighborhood of a triangle *)
epsilon=0.5;
RegTneigh = ImplicitRegion[Norm[RegionNearest[RegT, {x, y}] - {x, y}, 2] <= epsilon, {x, y}]
(* Plotting the region (I don't know how to simply plot RegTneigh) *)
RegionPlot[Norm[RegionNearest[RegT, {x, y}] - {x, y}, 2] <= 0.5, {x, -2, 2}, {y, -1, 2}, ImagePadding -> 30, PlotPoints -> 30]
(* Checking the area of the region using f(x,y) = 1 *)
NIntegrate[1, {x, y} [Element] RegTneigh]