I wan't to identify a parameter in a first oder differential equation. My goal is proof of the calculation principle i use. First I calculate a response where the paramater is set to 0.3. Later this should be the result of an identification (optimisation)
g[b_]:=Module[{y,t,opl},
opl=Map[
NDSolve[{y'[t]+b y[t]==6,y[0]==0.0},y,{t,0,50}][[1,1,2]][#]&,
Range[0,50]
];
opl
]
Calculation of the response gives:
result = g[0.3]
{0.,5.18364,9.02377,11.8686,13.9761,15.5374,16.694,17.5509,18.1856,18.6559,19.0043,19.2623,19.4535,19.5952,19.7001,19.7778,19.8354,19.8781,19.9097,19.9331,19.9504,19.9633,19.9728,19.9798,19.9851,19.9889,19.9918,19.9939,19.9955,19.9967,19.9975,19.9982,19.9986,19.999,19.9993,19.9994,19.9996,19.9997,19.9998,19.9998,19.9999,19.9999,19.9999,20.,20.,20.,20.,20.,20.,20.,20.}
The norm for the optimization is defined as:
h[x_]:=Norm[g[x]-result]
The optimization function to find the paramater 'x'
NMinimize[h[x],x]
This should give the value x=0.3 and the Norm = 0. But i get an error:
NDSolve::nlnum: "The function value {6-0.000102648\ x} is not a list of numbers with dimensions {1} at {t$45265,y$45265[t$45265]} = {0.00001710798632092067`,0.00010264791792552401`"
What could be wrong. I used several different optimization functions but the error stays.
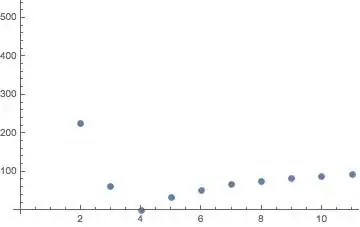
The function g behaves well as can be seen below:
ListPlot[Map[Norm[g[#]-result]&,Range[0,1,0.1]]]
h:h[x_?NumericQ] :=...See this answer. Now, it should be clear thathwill be minimized atx = 0.3by the definition ofhandresult. Maybe there's a typo somewhere? – Michael E2 Nov 04 '14 at 20:04x = 0.3remark. I forgot you had mentioned it in the question. Sorry. But the?NumericQtrick still looks like the answer. – Michael E2 Nov 04 '14 at 20:19