Updated Response
The internal name of System.Collections.Generic.List is "mangled". We can see what that internal name is by using NETTypeInfo:
NETTypeInfo[LoadNETAssembly["mscorlib.dll"], "Classes", "*Generic.List*"]
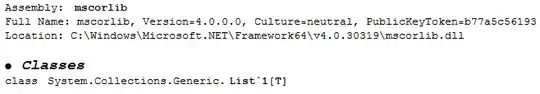
We can see that the internal name is System.Collections.Generic.List`1[T].
We can create objects of this type directly with NETNew provided we replace the placeholder type name T with the actual element type:
Needs["NETLink`"]
InstallNET[];
$list = NETNew["System.Collections.Generic.List`1[System.String]"];
$list@Add["xyz"]
$list@Add["mno"]
$list@Add["abc"]
$list@Sort[]
$list@ToArray[]
(* {"abc","mno","xyz"} *)
Original Response
In .NET, generic types cannot be instantiated directly. We must first create a specific type that specifies the generic type parameters. This is done using Type.MakeGenericType.
First we must obtain a reference to the List type. The NETLink wrapper is not enough -- we must use GetTypeObject to recover the native .NET type object:
Needs["NETLink`"]
$genericListType =
LoadNETType["System.Collections.Generic.List`1"] // GetTypeObject;
Note carefully that the internal class name ends with List`1, as shown by the information returned by the mscorlib NETTypeInfo call exhibited in the question.
We then need to load the type for the list elements. For this example, we will use the String type:
$stringType = LoadNETType["System.String"] // GetTypeObject;
Now we can create a dynamic type representing a list of strings:
$stringListType = $genericListType@MakeGenericType[{$stringType}];
Finally, we can create a list of strings and operate upon it:
$list = NETNew[$stringListType];
$list@Add["xyz"]
$list@Add["mno"]
$list@Add["abc"]
$list@Sort[]
$list@ToArray[]
(* {"abc","mno","xyz"} *)
