If you take a (labelled, oriented) 2 component link, it has a symmetry group which is a subgroup of the 16 element group $Z2 \times (Z2 \times Z2 \ltimes S_2)$ (mirror, reverse each component, swap the components). With Parsley, Cornish, and Mastin (http://arxiv.org/abs/1201.2722) I compiled a table of the frequency with which each conjugacy class of subgroups of this group comes up as a symmetry group for links up to 14 crossings.
Interestingly, the full group never came up as a symmetry group! Can a 2 component link ever have the full 16 element group? Is there some obstruction to this? Can anyone propose an example link?
Edit: A non split example. It is easy to construct split ones!
Clarification: The traditional symmetry group is the mapping class group $MCG(S^3,L)$. The symmetry group I want is the image of that group under the homomorphism $MCG(S^3,L) \rightarrow MCG(S^3) \times MCG(L)$, which is the 16 element group above. So another way to ask the question would be: can this homomorphism ever be surjective?
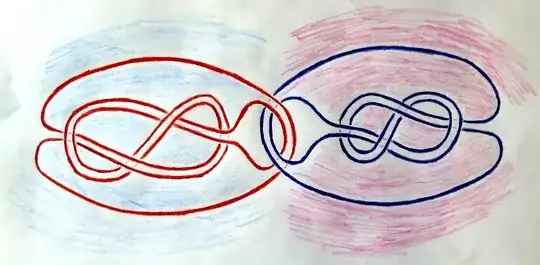
 and splice two figure-8 knots against it. You'd splice the knots against the red and purple components, respectively.
and splice two figure-8 knots against it. You'd splice the knots against the red and purple components, respectively.