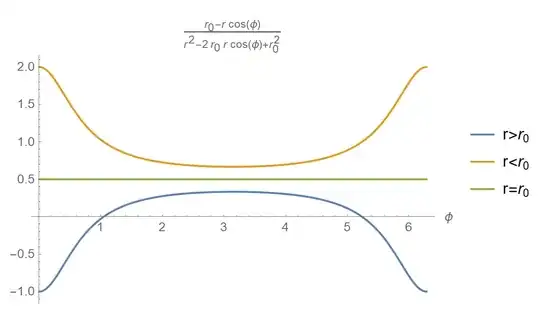
I'm trying to understand the deflection of light due to an axially symmetric gravitational lens following chapter 2.3 of these Heidelberg lecture notes. In doing so, I encounter the integral (2.12 a)
$$\int_0^{2\pi} \frac{r - r'\cos(\phi)}{r^2 + r'^2 - 2rr'\cos(\phi)}\,d\phi$$
which apparently vanishes for $r'>r$ and is $2\pi/r$ for $r'<r$. I've tried to understand how this answer comes about, but to no avail. I couldn't find it in an integral table and I can't get Mathematica to give me a useful answer unless I plug in specific values for $r,r'$.