I can reproduce your problem using next simple Powershell script
$RatedName = "šöü" # set sample string
$FormDName = $RatedName.Normalize("FormD") # its Canonical Decomposition
$FormCName = $FormDName.Normalize("FormC") # followed by Canonical Composition
# list each string character by character
($RatedName,$FormDName,$FormCName) | ForEach-Object {
$charArr = [char[]]$_
"$_" # display string in new line for better readability
# display each character together with its Unicode codepoint
For( $i=0; $i -lt $charArr.Count; $i++ ) {
$charInt = [int]$charArr[$i]
# next "Try-Catch-Finally" code snippet adopted from my "Alt KeyCode Finder"
# http://superuser.com/a/1047961/376602
Try {
# Get-CharInfo module downloadable from http://poshcode.org/5234
# to add it into the current session: use Import-Module cmdlet
$charInt | Get-CharInfo |% {
$ChUCode = $_.CodePoint
$ChCtgry = $_.Category
$ChDescr = $_.Description
}
}
Catch {
$ChUCode = "U+{0:x4}" -f $charInt
if ( $charInt -le 0x1F -or ($charInt -ge 0x7F -and $charInt -le 0x9F))
{ $ChCtgry = "Control" } else { $ChCtgry = "" }
$ChDescr = ""
}
Finally { $ChOut = $charArr[$i] }
"{0} {1,-2} {2} {3,5} {4}" -f $i, $charArr[$i], $ChUCode, $charInt, $ChDescr
}
}
# create sample files
$RatedName | Out-File "D:\test\1097217Rated$RatedName.txt" -Encoding utf8
$FormDName | Out-File "D:\test\1097217FormD$FormDName.txt" -Encoding utf8
$FormCName | Out-File "D:\test\1097217FormC$FormCName.txt" -Encoding utf8
"" # very artless draft of possible solution
Get-ChildItem "D:\test\1097217*" | ForEach-Object {
$y = $_.Name.Normalize("FormC")
if ( $y.Length -ne $_.Name.Length ) {
Rename-Item -NewName $y -LiteralPath $_ -WhatIf
} else {
" : file name is already normalized $_"
}
}
Above script is updated as follows: 1st shows more info on composed/decomposed Unicode characters i.e their Unicode names (see Get-CharInfo module); 2nd embedded very artless draft of possible solution.
Output from cmd prompt:
==> powershell -c D:\PShell\SU\1097217.ps1
šöü
0 š U+0161 353 Latin Small Letter S With Caron
1 ö U+00F6 246 Latin Small Letter O With Diaeresis
2 ü U+00FC 252 Latin Small Letter U With Diaeresis
šöü
0 s U+0073 115 Latin Small Letter S
1 ̌ U+030C 780 Combining Caron
2 o U+006F 111 Latin Small Letter O
3 ̈ U+0308 776 Combining Diaeresis
4 u U+0075 117 Latin Small Letter U
5 ̈ U+0308 776 Combining Diaeresis
šöü
0 š U+0161 353 Latin Small Letter S With Caron
1 ö U+00F6 246 Latin Small Letter O With Diaeresis
2 ü U+00FC 252 Latin Small Letter U With Diaeresis
: file name is already normalized D:\test\1097217FormCšöü.txt
What if: Performing the operation "Rename File" on target "Item: D:\test\1097217
FormDšöü.txt Destination: D:\test\1097217FormDšöü.txt".
: file name is already normalized D:\test\1097217Ratedšöü.txt
==> dir /b D:\test\1097217*
1097217FormCšöü.txt
1097217FormDšöü.txt
1097217Ratedšöü.txt
In fact, above dir output looks like 1097217FormDsˇo¨u¨.txt in cmd window and my unicode-aware browser composes strings as listed above but unicode analyzer shows the characters truly as well as the latest image:
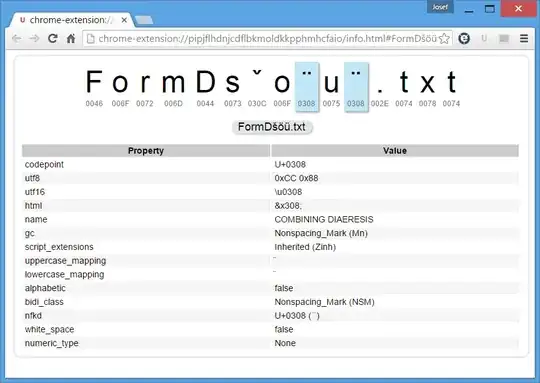
However, next example shows the problem in its full width: a for loop changes combining accents to normal ones:
==> for /F "delims=" %G in ('dir /b /S D:\test\1097217*') do @echo %~nxG & dir /B %~fG
1097217FormCšöü.txt
1097217FormCšöü.txt
1097217FormDsˇo¨u¨.txt
File Not Found
1097217Ratedšöü.txt
1097217Ratedšöü.txt
==>
Here's very artless draft of possible solution (see output above):
"" # very artless draft of possible solution
Get-ChildItem "D:\test\1097217*" | ForEach-Object {
$y = $_.Name.Normalize("FormC")
if ( $y.Length -ne $_.Name.Length ) {
Rename-Item -NewName $y -LiteralPath $_ -WhatIf
} else {
" : file name is already normalized $_"
}
}
(ToDo: invoke Rename-Item merely if necessary):
Get-ChildItem "D:\test\1097217*" | ForEach-Object {
$y = $_.Name.Normalize("FormC")
if ($true) { ### ToDo
Rename-Item -NewName $y -LiteralPath $_ -WhatIf
}
}
and its output (again, here are rendered composed strings and image below shows cmd window look unbiased):
What if: Performing the operation "Rename File" on target "Item: D:\test\1097217
FormCšöü.txt Destination: D:\test\1097217FormCšöü.txt".
What if: Performing the operation "Rename File" on target "Item: D:\test\1097217
FormDšöü.txt Destination: D:\test\1097217FormDšöü.txt".
What if: Performing the operation "Rename File" on target "Item: D:\test\1097217
Ratedšöü.txt Destination: D:\test\1097217Ratedšöü.txt".
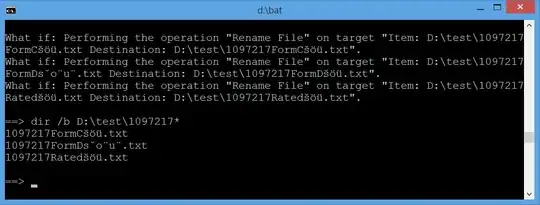
Updated cmd output




chcpin thecmdshell to set an appropriate code page. See chcp - Change the active console Code Page. The default code page is determined by the Windows Locale. – DavidPostill Jul 05 '16 at 17:33dir(Copy & Pastefromcmdwindow). @DavidPostillchcpwould not suffice; looks like there is displayed a Canonical or Compatibility Decompositionö(U+006FLatin Small Letter O followed byU+0308Combining Diaeresis) instead of theöcharacter (U+00F6Latin Small Letter O With Diaeresis). – JosefZ Jul 05 '16 at 20:07chcpbut couldn't get the name to show up correctly. It just changes the"to some other character like?. So it seems to have been originally saved with decomposition and command prompt shows the actual name, Windows Explorer combines it back on the fly. – nixer Jul 06 '16 at 08:52"(Quotation Mark) listed in a file name as this character is reserved (disallowed in a filename) by Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces article. Should apply to bothNTFSandReFSfile systems. Please run onelinerpowershell -c Get-ChildItem ^|ForEach-Object {$x=$_.Name; For ($i=0;$i -lt $x.Length; $i++) {\"{0} {1} {2}\" -f $x,$x[$i],[int]$x[$i]}}instead ofdirand [edit] again andCopy&Pasteonly relevant output lines (numbers should suffice). FYI"code is 34. – JosefZ Jul 07 '16 at 20:39