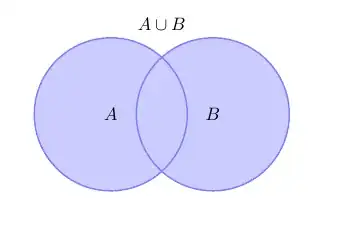
One possibility is to use the bounding box.
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{tikz}
\begin{document}
% Definition of circles
\def\firstcircle{(0,0) circle (1.5cm)}
\def\secondcircle{(0:2cm) circle (1.5cm)}
\colorlet{circle edge}{blue!50} \colorlet{circle area}{blue!20}
\tikzset{filled/.style={fill=circle area, draw=circle edge, thick},
outline/.style={draw=circle edge, thick}}
% Set A or B
\begin{tikzpicture}
\draw[filled] \firstcircle node {$A$}
\secondcircle node {$B$};
\node[anchor=south] at (current bounding box.north) {$A \cup B$};
\draw (current bounding box.north west) rectangle
(current bounding box.south east);
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}
If you need a somewhat larger box (this need not be the most elegant solution, but it works):
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{tikz}
\usetikzlibrary{calc}
\begin{document}
% Definition of circles
\def\firstcircle{(0,0) circle (1.5cm)}
\def\secondcircle{(0:2cm) circle (1.5cm)}
\colorlet{circle edge}{blue!50} \colorlet{circle area}{blue!20}
\tikzset{filled/.style={fill=circle area, draw=circle edge, thick},
outline/.style={draw=circle edge, thick}}
% Set A or B
\begin{tikzpicture}
\draw[filled] \firstcircle node {$A$}
\secondcircle node {$B$};
\node[anchor=south] at (current bounding box.north) {$A \cup B$};
\draw ($(current bounding box.north west)+(-1,1)$)
node [below right] {$U$}
rectangle ($(current bounding box.south east)+(1,-1)$);
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}