By using generating functions and snake-oil I got to
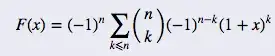
Also what is the implication of $\sum \limits_ {k<={n}}$?
I am told that this is equivalent to:
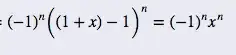
But I'm not sure how to do that step, thanks for the help!
By using generating functions and snake-oil I got to
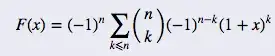
Also what is the implication of $\sum \limits_ {k<={n}}$?
I am told that this is equivalent to:
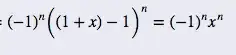
But I'm not sure how to do that step, thanks for the help!
It’s the binomial theorem,
$$(a+b)^n=\sum_{k\le n}\binom{n}ka^kb^{n-k}\;.$$
Now let $a=1+x$ and $b=-1$.
In this case taking the sum over $k\le n$ is equivalent to taking it from $k=0$ to $k=n$: by definition $\binom{n}k=0$ if $k<0$.