show that $$\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac {(\sin x) (x^2+a^2)}{x(x^2+b^2)}dx=\frac{\pi(a^2+e^{-b}(b^2-a^2))}{b^2}$$
for every $a,b>0$
thanks for all
show that $$\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac {(\sin x) (x^2+a^2)}{x(x^2+b^2)}dx=\frac{\pi(a^2+e^{-b}(b^2-a^2))}{b^2}$$
for every $a,b>0$
thanks for all
Consider the contour integral
$$\oint_C dz \frac{(z^2+a^2) e^{i z}}{z (z^2+b^2)}$$
where $C$ is the semicircular contour of radius $R$ in the upper half-plane, with an additional semicircular contour of radius $\epsilon$ centered at the origin, jutting into the upper half-plane.
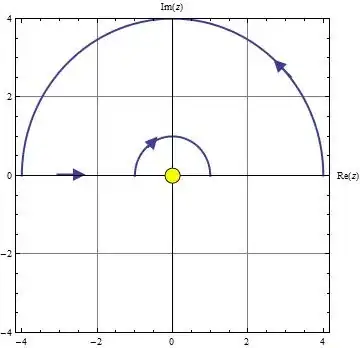
The contour integral is equal to
$$\int_{-R}^{-\epsilon} dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) e^{i x}}{x (x^2+b^2)} + i \epsilon \int_{-\pi}^0 d\phi e^{i \phi} \frac{(a^2+\epsilon^2 e^{i 2 \phi}) e^{i \epsilon e^{i \phi}}}{\epsilon e^{i \phi} (b^2+\epsilon^2 e^{i 2 \phi})}+\\\int_{\epsilon}^R dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) e^{i x}}{x (x^2+b^2)}+i R \int_0^{\pi} d\theta e^{i \theta}\frac{(a^2+R^2 e^{i 2 \theta}) e^{i R e^{i \theta}}}{Re^{i \theta} (b^2+R^2 e^{i 2 \theta})} $$
We take the limit as $R \to \infty$ and $\epsilon \to 0$ and get
$$PV \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) e^{i x}}{x (x^2+b^2)} - i \pi \frac{a^2}{b^2}$$
Note that the magnitude of fourth integral vanishes as
$$2 \int_0^{\pi/2} e^{-R \sin{\theta}} \le 2 \int_0^{\pi/2} e^{-2 R \theta/\pi} \le \frac{\pi}{R}$$
as $R \to \infty$. By the residue theorem, the contour integral is equal to $i 2 \pi$ times the residue of the pole at $z=i b$. Therefore
$$PV \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) e^{i x}}{x (x^2+b^2)} = i \pi \frac{a^2}{b^2} - i 2 \pi \frac{(a^2-b^2) e^{-b}}{2 b^2}$$
Similarly,
$$PV \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) e^{-i x}}{x (x^2+b^2)} = -i \pi \frac{a^2}{b^2} + i 2 \pi \frac{(a^2-b^2) e^{-b}}{2 b^2}$$
Therefore,
$$\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} dx \, \frac{(x^2+a^2) \sin{x}}{x (x^2+b^2)} = \pi \frac{a^2}{b^2} - \pi \frac{(a^2-b^2) e^{-b}}{ b^2}$$
which is equivalent to the stated result.