I would like to understand, how to obtain gradients of the PDE solution obtained with NDSolve. To be precise let us consider a Laplace equation from one of the examples:
Clear[x, y, f];
Needs["NDSolve`FEM`"]
emesh = ToElementMesh[Disk[]];
f = NDSolveValue[{Derivative[0, 2][u][x, y] +
Derivative[2, 0][u][x, y] == 0,
DirichletCondition[u[x, y] == Sin[x y], True]},
u, {x, y} ∈ emesh]
This returns the interpolation function which one can plot and integrate:
NIntegrate[f[x, y], {x, y} ∈ emesh]
(* 1.52794*10^-8 *)
Plot3D[f[x, y], {x, y} ∈ emesh]
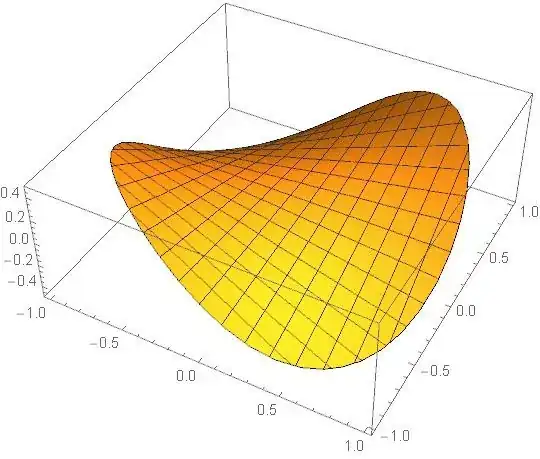
This, however, does not work:
g[x_, y_] := D[f[x, y], x];
Plot3D[g[x, y], {x, y} ∈ emesh]
Since
Integratedoes not work on this result, onlyNIntegratedoes, the problem is probably that one needs to apply a numeric derivative. What and how?
