
Why does Mathematica and Wolfram|Alpha give different results based upon the same code?
I know Wolfram|Alpha's 7.85 is correct.

Why does Mathematica and Wolfram|Alpha give different results based upon the same code?
I know Wolfram|Alpha's 7.85 is correct.
Artes' guess seems basically right. Here is a way to reach the correct result. First, the antiderivative returned by Mathematica:
i0 = FullSimplify[
Integrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], t],
t > 0]
(* (2 (Sqrt[16 - 2 I (-5 I + Sqrt[11]) t^2] Sqrt[8 + I (5 I + Sqrt[11]) t^2] (
5 (-5 I + Sqrt[11]) EllipticE[ArcSin[1/2 t Root[9 - 5 #1^2 + #1^4 &, 4]],
1/18 (7 - 5 I Sqrt[11])] -
(11 I + 5 Sqrt[11]) EllipticF[ArcSin[1/2 t Root[9 - 5 #1^2 + #1^4 &, 4]],
1/18 (7 - 5 I Sqrt[11])]) +
9/2 t (16 - 20 t^2 + 9 t^4) Root[36 + 10 #1^2 + #1^4 &, 3])) /
(27 Sqrt[(-5 - I Sqrt[11]) (16 - 20 t^2 + 9 t^4)]) *)
If we add to Pi to the two ArcSin expressions in i0, we get another antiderivative:
i1 = i0 /. a_ArcSin :> Pi + a;
D[i0, t] // FullSimplify[#, t > 0] &
D[i1, t] // FullSimplify[#, t > 0] &
(* Sqrt[16 - 20 t^2 + 9 t^4]
Sqrt[16 - 20 t^2 + 9 t^4] *)
It turns out that i1 is the continuation of i0:
Plot[{i0, i1}, {t, 0, 2},
PlotStyle -> {Directive[Thick, Blue], Directive[Thick, Red]}]
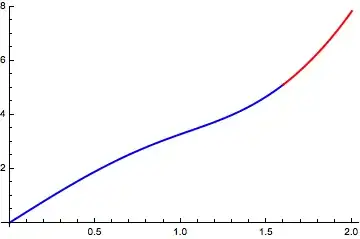
Hence,
(i1 /. t -> 2.) - (i0 /. t -> 0.)
(* 7.847 - 8.88178*10^-16 I *)
yields the correct (approximate) result.
Such are the pitfalls of elliptic integrals and their symbolic antiderivatives, I suppose. NIntegrate bypasses antiderivatives and estimates the integral from the (real) values of the integrand. It should never encounter such problems.
Further analysis
The plots below show the discontinuities in the EllipticE and EllipticF that lead to the incorrect value for Integrate. The discontinuities violate the conditions necessary to apply the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (an antiderivative is by definition supposed to be differentiable and therefore continuous).
{x0, x1} = FixedPoint[ (* find the discontinuity *)
Function[{x}, If[Im@Chop[i0 /. t -> x] != 0, {First[#], x}, {x, Last[#]}]][Mean[#]] &,
{1.599, 1.6}]
Table[
With[{part = part, ell = ell},
ContourPlot[
part[ell[ArcSin[1/2 t Root[9 - 5 #1^2 + #1^4 &, 4]],
1/18 (7 - 5 I Sqrt[11])]] /. t -> x + I y,
{x, 0, 2}, {y, -1, 1},
MaxRecursion -> 3, PlotPoints -> 25,
AxesOrigin -> {x0, 0}, Axes -> True,
AxesStyle -> Directive[Thin, Red], PlotLabel -> part@ell]
],
{ell, {EllipticE, EllipticF}}, {part, {Re, Im}}] // GraphicsGrid
(* {1.5991767250934696`, 1.5991767250934699`} *)

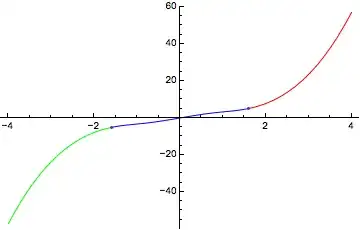
To get the real-valued antiderivative, piece together different branches:
anti = Piecewise[{
{i0, -x0 <= t <= x0},
{i0 /. a_ArcSin :> Pi + a, t >= x1},
{i0 /. a_ArcSin :> -Pi + a, t <= -x1}},
Indeterminate];
Plot[anti, {t, -4, 4},
Mesh -> {{-x0, x0}}, MeshShading -> {Green, Blue, Red}]
Integrate[f[t], t] (with no interval for t). You may know it by a different name.
– Michael E2
Oct 12 '13 at 11:24
This does not really answer the question as to why Mathematica's Integrate yields an apparently wrong answer. This simply states why the two answers are different. It seems Wolfram|Alpha does not attempt to do a symbolic integration (which is what your input asks for) before taking its numerical value. As I stated in my comment, using NIntegrate gives the correct answer similar to Wolfram|Alpha. So, in short, Wolfram|Alpha uses NIntegrate directly. Which is why the following input yields the right answer in Mathematica:
NIntegrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], {t, 0, 2}]
7.847
ArcSin, together they can produce unwanted imaginary result. There is another problem with real part but I guess they both could be resonably explained (as an inproper phase rule)
– Artes
Oct 11 '13 at 22:50
This is not an answer, but comparing the answer with Maple, and also showing step by step integration using Rubi, which might help point to where Mathematica went wrong.
r = Simplify@Integrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], t]
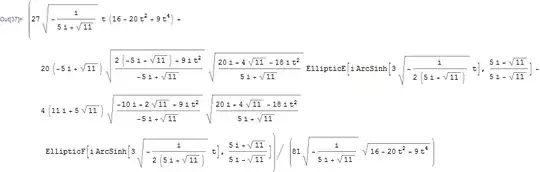
N[r /. t -> 2 - r /. t -> 0, 20]
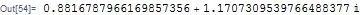
r:=int(sqrt( (2*t)^2+(4-3*t^2)^2),t=0..2);

evalf[20](r);
7.8469978240383303061+7.9695375019434005093*10^(-20)*I
F in the above is EllipticF and E is EllipticE. So both Maple and Mathematica have the answer in terms of Elliptic functions. To see step by step process, with the hope to better find where the bug happens, I used Rubi:
ShowSteps = True;
r = Int[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], t]





result = %;
N[result /. t -> 2 - result /. t -> 0, 20]

In one of those steps, the Integrate went wrong. Need more time to analyze.
I observed this behavior while at a training session at Wolfram Headquarters, and there seems to be an issue with using Integers here:
Integrate[Sqrt[(2. t)^2 + (4. - 3. t^2)^2], {t, 0, 2}] // N
(* 7.847 *)
Specifying Real numbers yields the correct result. I can only assume that Wolfram Alpha is performing this calculation with Real numbers as well.
Integrate[Sqrt[(2. t)^2 + (4. - 3. t^2)^2], {t, 0, 2}] returns unevaluated, so the // N basically converts it to an NIntegrate.
– Michael E2
Oct 12 '13 at 00:39
NIntegrate?
– bobthechemist
Oct 12 '13 at 00:47
NIntegrate gets it right. The problem is that Integrate takes an algebraic approach, and in this case, the interval $0 \le t \le 2$ seems to cross a branch cut of the antiderivative.
– Michael E2
Oct 12 '13 at 01:16
Okay, I'm slowly going through the questions involving elliptic integral evaluations. Yet again, none of the software mentioned in this thread have managed to produce a "clean" expression. For the benefit of future readers, here's a tidier closed form for your perusal:
N[2 (7 Sqrt[5] + 2 (10 EllipticE[2 π/3, 11/12] + EllipticF[2 π/3, 11/12])/Sqrt[3])/9, 20]
7.8469978240383303061
NIntegrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], {t, 0, 2}, WorkingPrecision -> 20]
7.8469978240383303060
NIntegrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], {t, 0, 2}]– RunnyKine Oct 11 '13 at 22:23Integrate[Sqrt[(2 t)^2 + (4 - 3 t^2)^2], t]; N[(%/.t->2), 20]gives the same wrong result. – Leo Fang Oct 11 '13 at 22:50